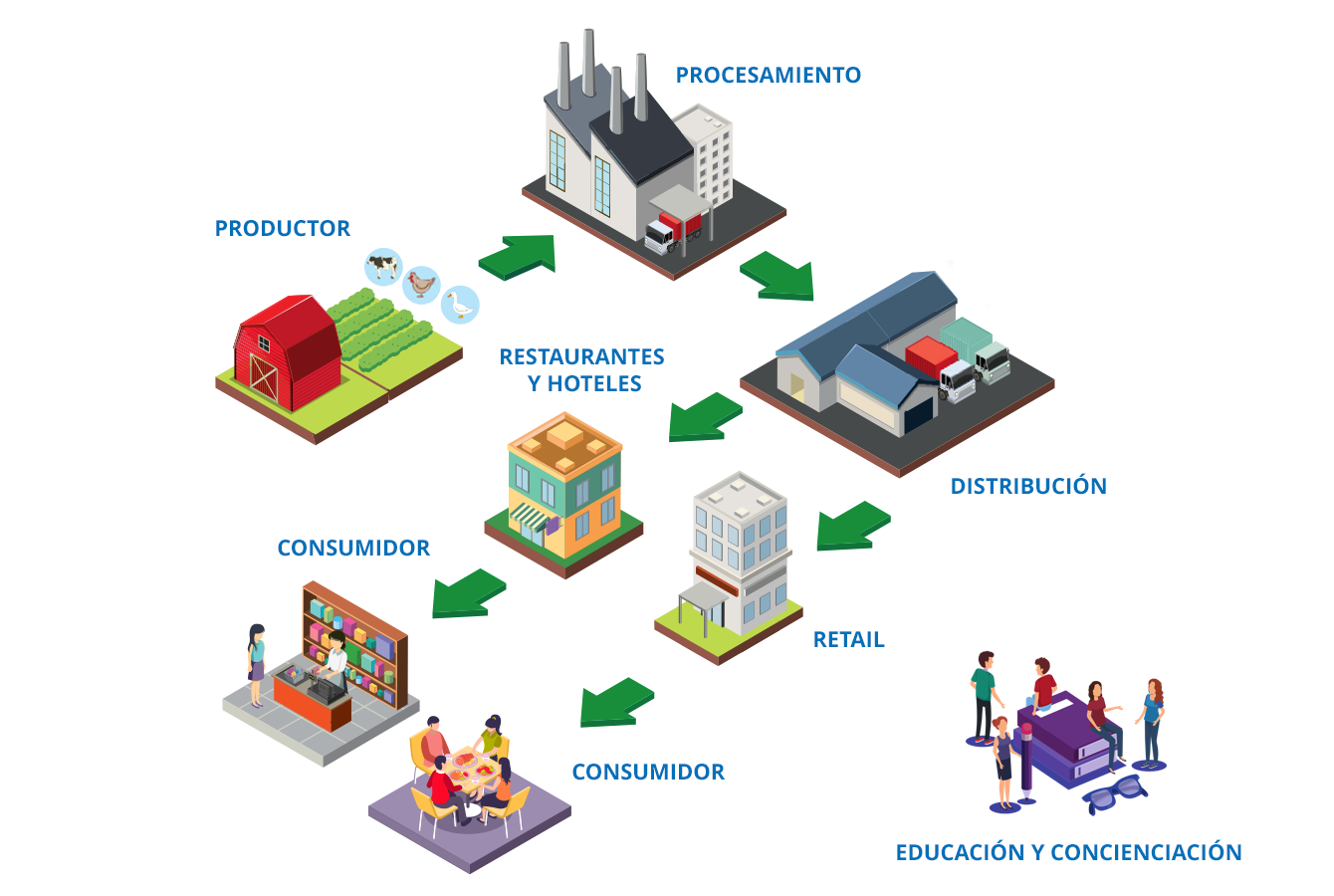
Food Transformation Hub
In this Food Transformation Hub, a space designed to provide useful information and encourage the exchange of best practices in the field of food sustainability, you will find success stories from the food and beverage sector that generate a positive impact on nature and climate change.
The examples presented are mainly from companies and organizations participating in the Sustainable Food Systems initiative, a platform dedicated to promoting the sustainable transformation of food systems. Each case includes an analysis of the specific challenge faced by the company or organization, the process to identify appropriate solutions, the actors involved, as well as the results obtained and lessons learned.
Do you want to share a best practice from your company that contributes to this sustainable transformation?
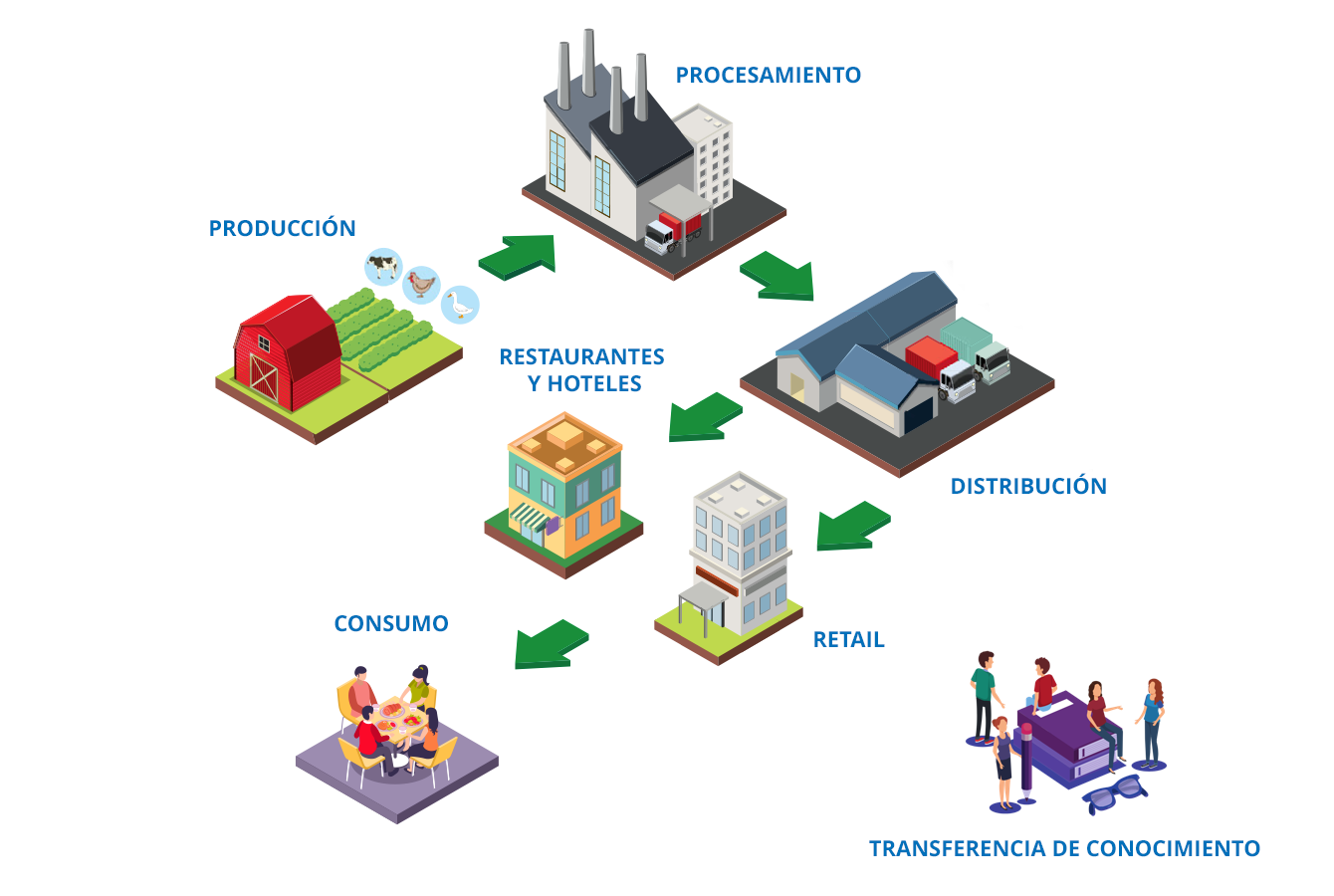
PRODUCTION
Baydiversity - Program for the conservation and restoration of biodiversity in agriculture.
Project for the conservation and improvement of biodiversity in agricultural farms, through the creation of habitats for birds, bats and other mammals, reptiles, amphibians, pollinators and other invertebrates, amphibians, pollinators and other invertebrates. Biodiversity hotspots are identified and evaluated, and based on this data, measures that also provide agricultural benefits, such as integrated pest control, pollination and erosion reduction, are prioritized. The project includes:
- Innovation: Demonstration projects carried out in La Rioja and Navarra (DIONISO) and in Seville through the Bayer Forward Farm.
- Collaborations: Biodiversity Node, Grefa, ASAJA Rioja, University of Seville, University of Cordoba, Polytechnic University of Valencia and Wild Life Ecodesign
- Techniques used: Monitoring of the impact of measures on biodiversity using standardized field methods, complemented with bioacoustic techniques. bioacoustics techniques that allow precise and continuous monitoring of the fauna.
The measures implemented have favored the presence of key species for the biological control of pests (birds of prey) and species typical of agricultural areas that are suffering a clear population decline (such as the Montagu's harrier). The installation of nest boxes has increased the presence of insectivorous birds such as coal tits and blue tits, and many of the shelter boxes installed have been occupied by bat species with an important impact on pest predation in crops such as olive groves and vineyards. An increase in beneficial invertebrates has also been observed.
- Difficulties encountered: Measures aimed at creating wildlife refuges have been well received, while those focused on habitat improvement have generated initial resistance. Another difficulty is the quantification of the impact on biodiversity over time, especially in the absence of a solid baseline data.
- Lessons for the Future: Need for integrated approach incorporating innovative services in the application of precision agriculture and regenerative agriculture, and aligned with biodiversity promotion practices.
From the pig to the pig's feet: a project for the revalorization of pig waste and by-products.
The great challenge for the food sector is to make the impact of its activity neutral. For this reason, Campofrío Frescos, Sigma's fresh meat business unit in Europe, is leading initiatives to promote its transition to a circular production model.
In 2023, Campofrío Frescos launched a project for the use and revaluation of pork by-products. In collaboration with the biotechnology company Horizon Products, it has built a porcine intestinal mucosa fractionation plant at its facilities for its subsequent transformation into heparin, a natural anticoagulant indicated for the prevention and treatment of thrombosis and considered one of the essential medicines by the World Health Organization (WHO).
The CH Biotec plant (a joint venture created for this project between Campofrío Frescos and Horizon Products) has the capacity to process more than 3,000 MT of porcine intestinal mucosa, which would generate approximately 150 billion units of heparin, the equivalent of about 30 million syringes or treatment for 2 million people.
Collaboration and synergy between companies and the contribution of knowledge by technology centers is key to the development of this type of project, as it considerably reduces investment costs and execution times, and the benefit not only affects the company itself, but also society as a whole.
The decarbonization ofhe world leader in the rice sector
The Ebro Group, a world leader in the rice sector and a wide international presence in the dry pasta businesspremiumand fresh pasta businesses, had the objective of measuring its carbon footprint as a basis for the definition of a decarbonization plan aligned with the environmental commitments acquired in its sustainability strategy.
With land use-related sectors accounting for more than 20% of global emissions, the company sought to respond to increasing regulatory pressure and customer demands.
With a complex international value chain, measuring the Ebro Group's Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions was a challenge in terms of stakeholder involvement (encompassing the group's more than 30 companies and their suppliers) and information availability.
PROJECT OBJECTIVES:
- Define a model that would allow the Ebro Group to measure its carbon footprint autonomously.
- Assess the implications of defining decarbonization targets at the Group level in the short term in line with SBTi sectoral requirements.
- Define a decarbonization plan for the Group's main European company.
- Evaluate the environmental and financial implications of the objectives to be defined.
- Percentage of the Ebro Group's total carbon footprint represented by its Scope 3 emissions: 96%.
- Number of Ebro Group companies covered by the footprint calculation exercise: >30
- Number of people involved in the training sessions on carbon footprint calculation: >50
- Bearing in mind the complexity of the Ebro Group's operations, the initial screening exercise served to focus efforts on the most relevant sources of emissions and companies within the Group.
- The complexity of the Ebro Group's supply chain made it very important to involve members of the various international subsidiaries through continuous training, focusing on the areas responsible for the supply and transportation of raw materials.
- In addition, taking into account that emissions associated with the supply of raw materials account for +75% of the Group's total carbon footprint, having detailed information on its environmental impact (extracted from HowGood, the most extensive database in the agri-food sector) made it possible to approach the calculation with an adequate level of precision, in line with reference standards such as SBTi FLAG.
- When addressing the Group's decarbonization plan, it was essential to be able to perform a financial impact analysis of the levers to be implemented in parallel to its environmental impact analysis in order to plan compliance with reference frameworks such as SBTi from the point of view of required investments and estimated savings.
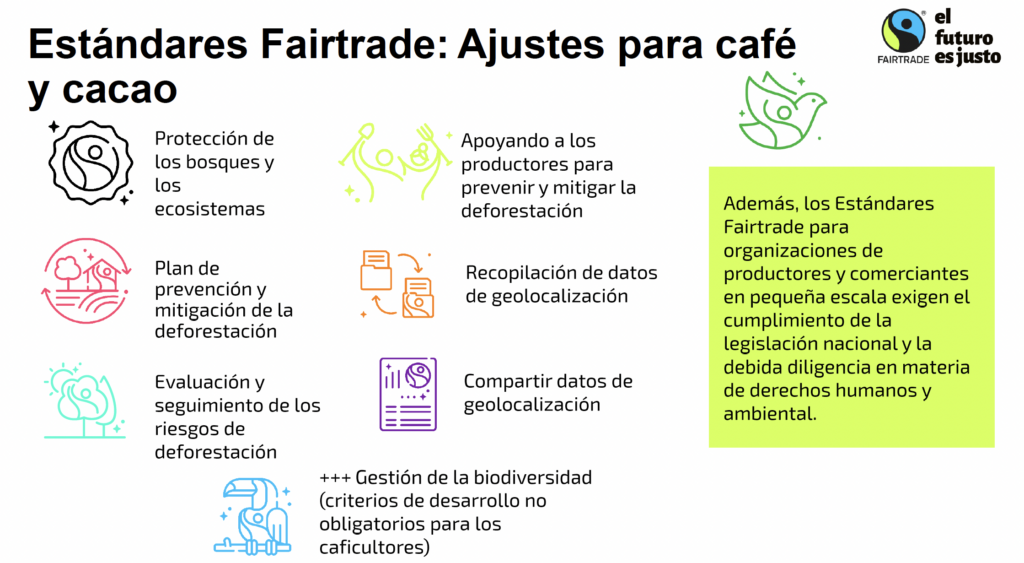
Fairtrade certification as a tool for EUDR compliance for coffee and cocoa
- Challenge: European Deforestation Regulation EUDR for the production and marketing of coffee and cocoa.
- Process: Fairtrade with its economic, social and environmental standards already prohibited the cultivation of coffee in deforested areas or at risk of forest degradation since December 2014 and cocoa since December 2018, updates its production and trading standards. Including analysis, monitoring and risk assessment, collection of geolocation data, compliance with national legislation of producing countries.
- Stakeholders involved: producers, traders and marketers along the chain.
- Qualitative Impact: updated production and marketing standards for coffee and cocoa. Update production and marketing standards. Includes risk analysis, monitoring and evaluation, geolocation data collection, compliance with national legislation.
- Quantitative Impact: Cocoa 400 producer organizations sent their geolocation data 38% validated. Coffee 600 producer organizations submitted 22% validated November 2024. Monitored by producer networks located in the Caribbean, South America, Africa and Asia.
Working in alliances with all actors in the value chain and the regulatory push is necessary to reduce poverty and improve living conditions in producer countries. Fairtrade through its certification standards, field projects and advocacy work reduces the risk of deforestation and promotes sustainable production.
Greening Communities for Sustainable Production
Greening Communities is a World Vision methodology aimed at reversing deforestation, land degradation and loss of productivity.
Our agricultural cooperation projects have been very successful with techniques such as Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration (recognized as an SDG best practice) or community-based disaster risk management. Reverdecer comunidades integrates ancestral practices with such techniques, working in collaboration with authorities and communities.
In Ethiopia 58,429 farmers rehabilitated 43,678 Ha of land using terracing, gully reclamation and FMNR; captured rainwater with ditches, wells and dams; planted more than 2M trees. As a result, 3,500 ha of pasture and 2,585 ha of irrigated land have been brought into production. Springs recovered and biodiversity increased; the lack of water for watering livestock was reduced by 82%. Agricultural productivity increased, and with it sales and household income. The number of months families go hungry per year decreased from 3.4 (2014) to 1.6 (2018), 93% of families reported not going hungry and the average family income doubled.
Combining reforestation and crops with Agriculture Climate Climate-Smart Agriculture all result in greater community cohesion, environmental improvements and increased quantity and quality of crops, livestock, forest products and natural resources for households to consume and sell, contributing to food security and resilience. quantity and quality of crops, livestock, forest products and natural resources for households to consume and sell, contributing to food security and resilience.
Dairy products that care for animal welfare
We are working hard to achieve one of the Group's environmental priorities: at the beginning of the dairy food value chain is the goal of enhancing the animal welfare of cattle, a requirement, moreover, of our consumers. In Spain, it involves the Milk Purchasing, Quality and Corporate Social Responsibility departments.
We started working on the Welfair® Animal Welfare certification in 2018. The Welfair® scheme entails the complete evaluation of animal welfare through the Welfare Quality and AWIN® protocols, as well as strict compliance with European legislation on animal welfare or higher, in those cases where stricter legislation exists locally. The farms are certified every year, and every three years the level of requirements is raised. It is very difficult to manage with the reality of the livestock sector in Spain, especially the smaller farms.
During 2024, more than 98% of our milk and more than 95% of the beef farms we collaborate with have been certified by AENOR in Animal Welfare. Welfair® Animal Welfare is the only independent certificate approved by IRTA. It is based on the Benchmarks Benchmarks Welfare Quality and AWIN® and comprehensively assesses and monitors the quality of animal welfare on farms (feeding, housing, health and behavior). Thanks to this certification, Lactalis Spain is the dairy company with the most certified dairy farms in Spain.
Milk is the main raw material from which we make our dairy foods. In 2024 alone, we will handle more than 900 million liters of milk in Spain. Having the objectives of training 100% of our technical field staff by 2023 and advising 100% of the livestock by 2025, has meant a reorganization of the entire milk purchasing department.
The greatest learning experience has been working on sustainability with all members of the chain. We have held meetings with farmers (in Mollerusa and Granada), as well as satisfaction surveys.
Vuelca Fácil, a new way to consume tuna with 35% less impact on global warming
In 2017, Nauterra set a challenge: to reinvent the iconic round can of tuna to better meet consumer needs, optimize resources in its manufacture and reduce food waste in its use. Through various studies and focus groups with consumers, four key aspects were defined: easy opening, the right amount of oil (73% did not incorporate leftover oil into the dish), maximum use of the tuna and sustainable packaging.
The project, which involved 5 years of work and an investment of 30 million euros, mobilized the entire company. The eco-design of the new packaging required the complete redesign of the production and packaging process at the Carballo plant (Galicia) and the development of the innovative Real Peel heat-sealing technology, in collaboration with specialized suppliers.
The development of this new packaging has been one of the most complex challenges in the history of Nauterra. Nauterra. Its success is due to exceptional collaboration between all areas of the company, from R&D to production, with each team contributing its expertise. The involvement of various technology suppliers was also key, allowing the production chain to be completely transformed. In addition, the consumer played an essential role, with 94% of respondents valuing this innovation as a differential in the canned food market.
The result, launched on the market in 2021, has been a more practical package that allows, through the overturn, to extract 100% of the product without the need to use a fork. In addition, it incorporates just the right amount of oil (15 g less) and the weight of the can has been reduced by 28% to 37% compared to traditional formats. A comparative life cycle analysis (LCA) confirmed its lower environmental impact in all the categories evaluated, and specifically a reduction of up to 35% in its impact on global warming.
Driving Sustainable Food Systems through Regenerative Agriculture at Nestlé
On our path to zero net emissions, Nestlé is committed to regenerative agriculture, as almost two-thirds of our emissions come from our raw materials. This model aims to conserve and restore agricultural land and its ecosystems, forming the basis for sustainable food production.
In Spain, we have 3 regenerative agriculture projects underway: Solís Responsable for tomato production in Vegas del Guadiana (Extremadura); cereal production in Castilla y León and Navarra for Nestlé Baby Food porridges; and milk production in the Cantabrian Coast, collaborating with farmers to optimize the production of forage crops for the production of infant milks, chocolates and Leche Condesada and Ideal.
Preserving natural resources such as water, improving soil health, promoting biodiversity and reducing the carbon footprint.
We use indicators such as the hectares in which we apply regenerative agriculture practices in each year, the % reduction of CO2eq in each year, and the % reduction of CO2eq in each year.
Other benefits such as the amount of fertilizers or herbicides used are also measured.
It is essential to train farmers with tools and knowledge to implement regenerative agriculture practices. Establish monitoring and evaluation systems to measure their impact and adjust measures as necessary. The support of public administrations and public-private collaboration are crucial to harmonize systems and promote these measures. In addition, there should be a harmonized policy for companies and farmers in the transition to this model of regenerative agriculture, as well as funding and incentive policies to facilitate this process.
Bringing technology and agriculture together to restore the Tagus river basin
The Tagus River stretches for more than 1,000 kilometers and is one of the most emblematic waterways in the Iberian Peninsula. It is vital for the water supply of several local communities that depend on the basin to meet their daily needs, as well as 33 endangered species. For years, the basin has been facing significant challenges due to the growing demand for water and the effects of climate change, which are intensifying water scarcity in the region.
Agrow presents a technological solution for irrigation digitalization to optimize water use in agriculture. A water saving and reinsertion project has been implemented in a total of 237 hectares of crops where an in-depth analysis of the specific conditions of each field and the water needs of the crops was carried out. As a result, specific recommendations are provided to optimize irrigation, improving productivity and water efficiency at the same time.
- Farmers were able to reduce water use by 27% in just one year. The impact of water efficiency was calculated through the measurement of water savings, where the water footprint of the crop is the main indicator of water consumption.
- The habitat of 33 endangered species that depend on the Tagus River ecosystem has been preserved, preserving biodiversity in the region.
- We were able to raise awareness in the agricultural sector about the water crisis and the possibility of improving irrigation practices through technology.
We have been able to understand the farmer's perspective, the water challenges they face and their view of water sustainability. As a result, we have learned that trust is the main factor on which these projects rely. Our commitment to developing the best technological tool that integrates the farmer's key needs is the pillar on which these savings are based. We have understood that the importance of the tool, the transmission of its operation and the confidence it guarantees in production are, together, our great differential.
PROCESSING
ACCELEREAT: Promoting sustainability and competitiveness in the value chain of new foods.
Aldelís identified two key challenges in the agri-food sector: the need to extend the shelf life of poultry products in a safe and sustainable way and the search for a sustainable alternative to traditional meat. To address these challenges, advanced technologies were implemented to reduce the microbial load in poultry meat, improving its safety and extending its shelf life. In parallel, in collaboration with BIOTECH FOOD, Aldelís is working on the development of products based on meat an innovative solution that significantly reduces the environmental footprint of meat production. This project involves internal R&D&I teams, technological partners such as AINIA and BIOTECH FOOD, and the support of the PERTE program. AccelerEAT.
The project, currently underway, focuses on implementing innovative technologies such as ultrasound and electrolyzed water to address sustainability and food safety challenges. These technologies seek to reduce environmental impact by reducing the carbon footprint, water consumption and eliminating chemical disinfectants, thus promoting more sustainable production. In addition, work is being done to extend the shelf life of meat products, reducing food waste and improving efficiency. The results are evaluated through life cycle analysis (LCA) and sustainability audits.
Collaboration between companies, technology centers and programs like PERTE AccelerEAT is key to implementing sustainable solutions in the food industry. Consumer acceptance depends on transparent communication about these benefits, highlighting the importance of involving them in the transition to responsible practices. A holistic approach that combines innovation, sustainability and collaboration is essential to address challenges such as climate change and food waste.
RETAIL
Too Good To Go, the biggest app to fight food waste
More than 2.5 billion tons of food are wasted every year, which accounts for 40% of the world's food production and is responsible for 10% of greenhouse gas emissions. Hence, reducing food waste is considered by experts to be the number one solution to curb climate change.
With the mission to offer solutions and to inspire and empower everyone to fight together against food waste, Too Good To Go is born, a social impact company responsible for the largest app in the world that connects users with food brands and manufacturers and thousands of restaurants, supermarkets and all kinds of food stores that sell their surplus food at very low prices to avoid the waste of all that food that is in perfect condition and that has not been sold through its usual channel.
Too Good To Go is operating in 19 countries. Since its launch in 2016 and thanks to the entire community of users, brands and establishments, more than 400 million food packs that would otherwise have been wasted have already been saved through the app. Thanks to a study by Mérieux Nutrisciences | Blonk and validated by experts from Oxford University and WRAP, each pack saved avoids the emission of 2.7 kilos of CO2e and the waste of 810 liters of water. The emission of more than 1 million tons of CO2e and the waste of 324 billion liters of water have already been avoided.
Food waste is a global problem of great dimensions that cannot be tackled from a single perspective, but requires multiple solutions and must be addressed in a comprehensive manner. To this end, it has been and continues to be essential to encourage and support the collaboration of all parts of the chain, in which each link, from the field to the table, as well as the institutions, plays its role and is a fundamental part in resolving challenges such as this one.
RESTAURANTS AND HOTELS
Reduction of waste food waste thanks to AI
As part of its commitment to responsible tourism, Iberostar Hotels & Resorts has placed the circular economy at the heart of its operations. Improved waste management and the reduction of food waste are key pillars of this strategy. In order to advance along this path, the company has incorporated 3R (Reduce - Reuse - Recycle) teams in its hotels, made up of more than 250 people dedicated exclusively to waste management.
To reduce food waste, Iberostar has implemented Winnow technology, a system based on artificial intelligence. Currently installed in the kitchens of 44 hotels, it allows chefs to measure and analyze in real time the amount and type of food being discarded, generating both environmental and economic benefits.
In the hotels where the Winnownowing Technology has been deployed Winnow technology has been implementedtechnology, Iberostar managed to avoid 921,800 kg of food waste in 2023, which represents a reduction of more than 10% compared to the previous year. In addition, the reports generated thanks to Winnow identify the main causes of waste and develop strategies to prevent it in the future. These results demonstrate the key role of technology in advancing the company's circularity objectives.
Improving quantitative measurement in hotels, relying on technology and fostering a sense of pride among the teams dedicated to this challenge were key to reducing food waste by 10% in 2023 and reducing waste sent to landfill by 56% between 2021 and 2023. However, collaboration with the destination's infrastructure remains essential: a large part of the waste that the company still sends to landfill could be revalued if the right infrastructure were in place, especially in the case of organic waste.
TRANSFER OF KNOWLEDGE
Plataforma Tierra: Driving Digital Transformation and Sustainability in the Agri-Food Sector
The Cajamar Group has launched Plataforma Tierraa knowledge community managed by its specialists in agronomy, innovation and agribusiness to improve the efficiency, profitability and sustainability of the agri-food chain.
Since its inception, it has been conceived as a meeting point for all actors in the agri-food sector, with services and tools that drive and promote innovation based on information and knowledge. Users and visitors to the platform can access various areas such as the following three:
- The innovation section incorporates diverse contents, referring to all sectors of the agri-food economy. It includes trends in innovation, results of research and applied innovation projects, new technologies or new products and services. Special attention is paid to information related to efficiency and sustainability.
- News is another section that gathers information and news from the food chain of interest to any professional in the sector that has an impact on profitability, sustainability or innovation.
- In the section on training shows the catalog of events, on-site and online, that Grupo Cajamar organizes or in which it collaborates directly. It facilitates registration and compiles all the technical information derived, both presentations and working material or videos of the sessions. The section is completed with an offer of online courses available to any user of the agri-food sector.
In addition, users receive, on a weekly basis, a free newsletter free of charge, information on new publications, upcoming events or news of interest, adapted to the interests they have previously expressed.
After four years of operation, Plataforma Tierra has established itself as the meeting point for professionals in the agri-food sector. The diversity of authors participating in Plataforma Tierra is a guarantee of independence and balance. Among those who participate in the development of the contents are dominated by experts from different disciplines and specializations, ranging from economics to agricultural and food production and health, with an increasingly relevant weight of digital technologies and tools to move towards an agriculture and industry of precision and efficiency. The technical team involved in the development of Plataforma Tierra's activities is important; however, most of the contributions come from outside the Cajamar Cooperative Group.
The work developed in this initiative has allowed the platform to receive close to 1,200,000 visits in 2024. Many of them came from the nearly 25,000 registered users. These followers have been able to enjoy more than 3,000 contents.
CONSUMO
Eliminación de los dosificadores de plástico
Retirada de los dosificadores de plástico en España, de todas las botellas de las distintas marcas del grupo, poniendo la sostenibilidad en el foco.
Diageo anunció este año la retirada gradual en España de los dosificadores de plástico de todo su porfolio de marcas. Una medida con la que prevé reducir más de 100 toneladas de plástico al año, correspondientes a eliminar los dosificadores en 21 millones de botellas cada año. Esta iniciativa forma parte de 'Spirit of Progress', la ambiciosa estrategia ESG del grupo con horizonte 2030.
Con ello, Diageo reafirma también su apuesta por la especialización y profesionalización del sector, promoviendo el empleo del vaso medidor y la estandarización de proporciones en cada tipo de consumición.
Pequeños cambios pueden ser decisivos: la retirada de los dispensadores de plástico de las botellas tiene un importante impacto en términos de reducción del uso de plástico y de las emisiones. Asimismo, a través de esta iniciativa la compañía eleva la experiencia de consumo al promover un servicio más preciso y de mayor calidad, tanto en establecimientos como en doméstico.
Todavía no hemos publicado casos sobre Distribución. Próximamente añadiremos ejemplos.


Driving Sustainable Food Systems through Regenerative Agriculture at Nestlé
On our path to zero net emissions, Nestlé is committed to regenerative agriculture, as almost two-thirds of our emissions come from our raw materials. This model aims to conserve and restore agricultural land and its ecosystems, forming the basis for sustainable food production.
In Spain, we have 3 regenerative agriculture projects underway: Solís Responsable for tomato production in Vegas del Guadiana (Extremadura); cereal production in Castilla y León and Navarra for Nestlé Baby Food porridges; and milk production in the Cantabrian Coast, collaborating with farmers to optimize the production of forage crops for the production of infant milks, chocolates and Leche Condesada and Ideal.


Dairy products that care for animal welfare
We are working hard to achieve one of the Group's environmental priorities: at the beginning of the dairy food value chain is the goal of enhancing the animal welfare of cattle, a requirement, moreover, of our consumers. In Spain, it involves the Milk Purchasing, Quality and Corporate Social Responsibility departments.
We started working on the Welfair® Animal Welfare certification in 2018. The Welfair® scheme entails the complete evaluation of animal welfare through the Welfare Quality and AWIN® protocols, as well as strict compliance with European legislation on animal welfare or higher, in those cases where stricter legislation exists locally. The farms are certified every year, and every three years the level of requirements is raised. It is very difficult to manage with the reality of the livestock sector in Spain, especially the smaller farms.


Driving Sustainable Food Systems through Regenerative Agriculture at Nestlé
On our path to zero net emissions, Nestlé is committed to regenerative agriculture, as almost two-thirds of our emissions come from our raw materials. This model aims to conserve and restore agricultural land and its ecosystems, forming the basis for sustainable food production.
In Spain, we have 3 regenerative agriculture projects underway: Solís Responsable for tomato production in Vegas del Guadiana (Extremadura); cereal production in Castilla y León and Navarra for Nestlé Baby Food porridges; and milk production in the Cantabrian Coast, collaborating with farmers to optimize the production of forage crops for the production of infant milks, chocolates and Leche Condesada and Ideal.
PRODUCTION
Driving Sustainable Food Systems through Regenerative Agriculture at Nestlé
Dairy products that care for animal welfare - Lactalis Spain
Title of the good practice
Title of the good practice
DISTRIBUTION
Title of the good practice
Title of the good practice
Title of the good practice
DISTRIBUTION
This is the central management area of the standard, as it involves the involvement of top management in the process and is key to conveying the message and defining the guidelines for responsible management at all organizational levels.
The requirements requested in this area are:
- Develop an Ethics Management Policy and publicize it.
- Define a Code of Conduct to guide corporate decisions.
- Establish a Social Responsibility Committee to coordinate the integration of CSR in the organization.
- Designate a person responsible for the organization's ethics management system.
- Establish a methodology to identify and manage environmental, social and governance risks.
- Define a social responsibility plan, with objectives and progress indicators.
- Identify stakeholders
- Develop an anti-corruption policy
- Conduct annual internal audits
- Conduct an annual Management Review process of the main aspects of the system.
- Disclose non-financial information through the available channels and, in particular, publish a sustainability/CSR report.
This is the central management area of the standard, as it involves the involvement of top management in the process and is key to conveying the message and defining the guidelines for responsible management at all organizational levels.
The requirements requested in this area are:
- Develop an Ethics Management Policy and publicize it.
- Define a Code of Conduct to guide corporate decisions.
- Establish a Social Responsibility Committee to coordinate the integration of CSR in the organization.
- Designate a person responsible for the organization's ethics management system.
- Establish a methodology to identify and manage environmental, social and governance risks.
- Define a social responsibility plan, with objectives and progress indicators.
- Identify stakeholders
- Develop an anti-corruption policy
- Conduct annual internal audits
- Conduct an annual Management Review process of the main aspects of the system.
- Disclose non-financial information through the available channels and, in particular, publish a sustainability/CSR report.
This is the central management area of the standard, as it involves the involvement of top management in the process and is key to conveying the message and defining the guidelines for responsible management at all organizational levels.
The requirements requested in this area are:
- Develop an Ethics Management Policy and publicize it.
- Define a Code of Conduct to guide corporate decisions.
- Establish a Social Responsibility Committee to coordinate the integration of CSR in the organization.
- Designate a person responsible for the organization's ethics management system.
- Establish a methodology to identify and manage environmental, social and governance risks.
- Define a social responsibility plan, with objectives and progress indicators.
- Identify stakeholders
- Develop an anti-corruption policy
- Conduct annual internal audits
- Conduct an annual Management Review process of the main aspects of the system.
- Disclose non-financial information through the available channels and, in particular, publish a sustainability/CSR report.
This is the central management area of the standard, as it involves the involvement of top management in the process and is key to conveying the message and defining the guidelines for responsible management at all organizational levels.
The requirements requested in this area are:
- Develop an Ethics Management Policy and publicize it.
- Define a Code of Conduct to guide corporate decisions.
- Establish a Social Responsibility Committee to coordinate the integration of CSR in the organization.
- Designate a person responsible for the organization's ethics management system.
- Establish a methodology to identify and manage environmental, social and governance risks.
- Define a social responsibility plan, with objectives and progress indicators.
- Identify stakeholders
- Develop an anti-corruption policy
- Conduct annual internal audits
- Conduct an annual Management Review process of the main aspects of the system.
- Disclose non-financial information through the available channels and, in particular, publish a sustainability/CSR report.